Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
石川 卓門*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 107(5), p.054426_1 - 054426_9, 2023/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study the temperature dependence of spin-Hall magnetoresistance (SMR) in antiferromagnetic-insulator/metal bilayer systems. We calculate the amplitude of the SMR signal by using a quantum Monte Carlo simulation and examine how the SMR depends on the amplitude of the spin, thickness of the antiferromagnetic-insulator layer, and randomness of the exchange interactions. Our results for simple quantum spin models provide a useful starting point for understanding SMR measurements on atomic layers of magnetic compounds.
 Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effect
Sn thin films by magneto-optical Kerr effect内村 友宏*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 佐藤 佑磨*; 竹内 祐太郎*; 金井 駿*; 武智 涼太*; 岸 桂輔*; 山根 結太*; DuttaGupta, S.*; 家田 淳一; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 120(17), p.172405_1 - 172405_5, 2022/04
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:84.45(Physics, Applied)We perform a hysteresis-loop measurement and domain imaging for 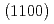 -oriented
-oriented  -Mn
-Mn Sn
Sn
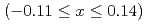 thin films using magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) and compare it with the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) measurement. We obtain a large Kerr rotation angle of 10 mdeg., comparable with bulk single-crystal Mn
thin films using magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) and compare it with the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) measurement. We obtain a large Kerr rotation angle of 10 mdeg., comparable with bulk single-crystal Mn Sn. The composition
Sn. The composition  dependence of AHE and MOKE shows a similar trend, suggesting the same origin, i.e., the non-vanishing Berry curvature in the momentum space. Magnetic domain observation at the saturated state shows that x dependence of AHE and MOKE is explained by an amount of reversible area that crucially depends on the crystalline structure of the film. Furthermore, in-depth observation of the reversal process reveals that the reversal starts with nucleation of sub-micrometer-scale domains dispersed in the film, followed by a domain expansion, where the domain wall preferentially propagates along the
dependence of AHE and MOKE shows a similar trend, suggesting the same origin, i.e., the non-vanishing Berry curvature in the momentum space. Magnetic domain observation at the saturated state shows that x dependence of AHE and MOKE is explained by an amount of reversible area that crucially depends on the crystalline structure of the film. Furthermore, in-depth observation of the reversal process reveals that the reversal starts with nucleation of sub-micrometer-scale domains dispersed in the film, followed by a domain expansion, where the domain wall preferentially propagates along the ![$$[11bar{2}0]$$](/search/images/ERNTCMK2MJQXE4ZSPUYF0JA.gif) direction. Our study provides a basic understanding of the spatial evolution of the reversal of chiral-spin structure in non-collinear antiferromagnetic thin films.
direction. Our study provides a basic understanding of the spatial evolution of the reversal of chiral-spin structure in non-collinear antiferromagnetic thin films.
荒木 康史; 家田 淳一
Physical Review Letters, 127(21), p.277205_1 - 277205_7, 2021/12
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:54.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)強いスピン-軌道相互作用の下での電子系には、運動量空間内のトポロジーが発現する。この電子系トポロジーは磁性体中の磁気構造に対して、乱れや熱揺らぎに影響されない電場誘起トルクを与える。本研究では現象論的なトルクの分類に基づき、バンドトポロジーとトルクの間の直接的な関係を示す。内因性異常ホール効果と同様に、トルクにもまた、非平衡輸送電流に依らず異常速度に起因した内因的効果が現れる。特に本論文では、磁気構造内でのみ現れる内因的トルクの存在を明らかにし、これを「トポロジカルホールトルク(THT)」と呼ぶ。このTHTはバルク結晶中で現れ、界面や表面といった構造を用いる必要がないものである。数値モデルの計算に基づき、金属強磁性体中での従来のスピン移行トルクと比較して、このTHTは非常に大きなトルクを与えることを明らかにする。特に金属強磁性体 における実験で報告されていた巨大な電流誘起トルクは、このTHTとして理解できることを示す。
における実験で報告されていた巨大な電流誘起トルクは、このTHTとして理解できることを示す。
竹内 祐太郎*; 山根 結太*; Yoon, J.-Y.*; 伊藤 隆一*; 陣内 佛霖*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 深見 俊輔*; 大野 英男*
Nature Materials, 20(10), p.1364 - 1370, 2021/10
被引用回数:84 パーセンタイル:98.68(Chemistry, Physical)Electrical manipulation of magnetic materials by current-induced spin torque constitutes the basis of spintronics. Recent studies have demonstrated electrical controls of ferromagnets and collinear antiferromagnets by spin-orbit torque (SOT). Here we show an unconventional response to SOT of a non-collinear antiferromagnet, which has recently attracted great attention owing to large anomalous Hall effect despite vanishingly small net magnetization. In heterostructures with epitaxial non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn Sn, we observe a characteristic fluctuation of Hall resistance, which is attributed to a persistent rotation of chiral-spin structure of Mn
Sn, we observe a characteristic fluctuation of Hall resistance, which is attributed to a persistent rotation of chiral-spin structure of Mn Sn driven by SOT. We find that level of the fluctuation that varies with sample size represents the number of magnetic domains of Mn
Sn driven by SOT. We find that level of the fluctuation that varies with sample size represents the number of magnetic domains of Mn Sn. In addition, Mn
Sn. In addition, Mn Sn thickness dependence of critical current reveals that SOT generated by small current density below 20 MA cm
Sn thickness dependence of critical current reveals that SOT generated by small current density below 20 MA cm effectively acts on the chiral-spin structure even in thick Mn
effectively acts on the chiral-spin structure even in thick Mn Sn above 20 nm. The results provide unprecedented pathways of electrical manipulation of magnetic materials, offering new-concept spintronics devices with unconventional functionalities and low-power consumption.
Sn above 20 nm. The results provide unprecedented pathways of electrical manipulation of magnetic materials, offering new-concept spintronics devices with unconventional functionalities and low-power consumption.
 Sn
Sn thin films
thin filmsYoon, J.-Y.*; 竹内 祐太郎*; DuttaGupta, S.*; 山根 結太*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
AIP Advances (Internet), 11(6), p.065318_1 - 065318_6, 2021/06
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:78.56(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We investigate the relationship between structural parameters, magnetic ordering, and the anomalous Hall effect (AHE) of Mn Sn
Sn (
(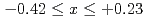 ) thin films annealed at various temperature
) thin films annealed at various temperature 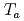 . The crystal structure changes with
. The crystal structure changes with  and
and 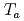 and at
and at 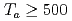
 C near the stoichiometric composition (
C near the stoichiometric composition (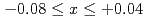 ) epitaxial single-phase
) epitaxial single-phase  0
0 -Mn
-Mn Sn
Sn (
(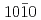 ) is obtained. At room temperature, a larger AHE is obtained when the single-phase epitaxial Mn
) is obtained. At room temperature, a larger AHE is obtained when the single-phase epitaxial Mn Sn with the lattice constant closer to that of bulk is formed. The temperature dependence of the AHE shows different behaviors depending on
Sn with the lattice constant closer to that of bulk is formed. The temperature dependence of the AHE shows different behaviors depending on 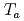 and can be explained by considering the variation of magnetic ordering. A close inspection into the temperature and composition dependence suggests a variation of magnetic phase transition temperature with composition and/or a possible correlation between the AHE and Fermi level position with respect to the Weyl points. Our comprehensive study would provide the basis for utilizing the unique functionalities of non-collinear antiferromagnetic materials.
and can be explained by considering the variation of magnetic ordering. A close inspection into the temperature and composition dependence suggests a variation of magnetic phase transition temperature with composition and/or a possible correlation between the AHE and Fermi level position with respect to the Weyl points. Our comprehensive study would provide the basis for utilizing the unique functionalities of non-collinear antiferromagnetic materials.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023219_1 - 023219_15, 2021/06
本論文では、トポロジカルディラック半金属(TDSM)表面のギャップレス状態を介した、長距離スピン伝送を理論面から提案する。次世代のスピントロニクス素子の構築のためには、散逸の少ないスピン流を実現することが必要である。主要なスピン流のキャリアは金属中の伝導電子や磁性絶縁体中のスピン波であるが、これらはジュール熱やギルバート緩和により伝播距離が制限される問題がある。本研究ではTDSM(Cd As
As , Na
, Na Bi等)のスピン・ヘリカルな表面状態が、乱れに対して頑強である性質を用いて、低散逸で長距離のスピン輸送を提案する。2つの磁性絶縁体とTDSMの接合系を考え、一方の磁性体の磁化ダイナミクスにより、TDSM表面を介して他方の磁性体に注入されるスピン流に注目する。表面における輸送理論と、格子模型による実時間発展シミュレーションを併用することにより、TDSM表面を流れるスピン流は準量子化された値をとり、その値は界面の微視的な結合の構造によらないことを示す。さらに、このスピン流は長距離においても乱れに対して強いことを示し、TDSMがスピントロニクス素子へ応用可能な表面状態をもつことを提案する。
Bi等)のスピン・ヘリカルな表面状態が、乱れに対して頑強である性質を用いて、低散逸で長距離のスピン輸送を提案する。2つの磁性絶縁体とTDSMの接合系を考え、一方の磁性体の磁化ダイナミクスにより、TDSM表面を介して他方の磁性体に注入されるスピン流に注目する。表面における輸送理論と、格子模型による実時間発展シミュレーションを併用することにより、TDSM表面を流れるスピン流は準量子化された値をとり、その値は界面の微視的な結合の構造によらないことを示す。さらに、このスピン流は長距離においても乱れに対して強いことを示し、TDSMがスピントロニクス素子へ応用可能な表面状態をもつことを提案する。
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(2), p.023195_1 - 023195_11, 2020/05
We theoretically manifest that the edge of a quantum spin Hall insulator (QSHI), attached to an insulating ferromagnet (FM), can realize a highly efficient spin-to-charge conversion. Based on a one-dimensional QSHI-FM junction, the electron dynamics on the QSHI edge is analyzed, driven by a magnetization dynamics in the FM. Under a large gap opening on the edge from the magnetic exchange coupling, we find that the spin injection into the QSHI edge gets suppressed while the charge current driven on the edge gets maximized, demanded by the band topology of the one-dimensional helical edge states.
Chen, Z. Q.; 山本 春也; 前川 雅樹; 河裾 厚男; Yuan, X. L.*; 関口 隆史*
Journal of Applied Physics, 94(8), p.4807 - 4812, 2003/10
被引用回数:169 パーセンタイル:96.7(Physics, Applied)水熱法によって育成された酸化亜鉛の格子欠陥の熱的性質を陽電子消滅,X線回折,ラザフォード後方散乱,カソードルミネッセンス及びホール測定を用いて研究した。陽電子寿命測定により育成直後には亜鉛原子空孔が存在していることが明らかになった。陽電子寿命のアニール挙動から亜鉛亜鉛原子空孔は、600 Cの熱処理によって消失することがわかった。X線回折ピーク幅及びラザフォード後方散乱収率も同様に低下することが知られた。1000
Cの熱処理によって消失することがわかった。X線回折ピーク幅及びラザフォード後方散乱収率も同様に低下することが知られた。1000 C以上の熱処理によって陽電子寿命が増加することがわかり、これより亜鉛原子空孔が形成することが示された。しかしながら、X線回折ピーク幅は1000
C以上の熱処理によって陽電子寿命が増加することがわかり、これより亜鉛原子空孔が形成することが示された。しかしながら、X線回折ピーク幅は1000 Cの熱処理後もさらに狭くなり、結晶性の向上を示した。自由電子密度は、1200
Cの熱処理後もさらに狭くなり、結晶性の向上を示した。自由電子密度は、1200 C迄の熱処理で連続的に増加した。この結果は、アクセプターとして作用する亜鉛原子空孔よりも余計にドナーが生成することを示している。カソードルミネッセンス測定の結果、紫外発光強度が熱処理温度とともに増加することがわかった。以上のように、酸化亜鉛の結晶性は600
C迄の熱処理で連続的に増加した。この結果は、アクセプターとして作用する亜鉛原子空孔よりも余計にドナーが生成することを示している。カソードルミネッセンス測定の結果、紫外発光強度が熱処理温度とともに増加することがわかった。以上のように、酸化亜鉛の結晶性は600 Cから1200
Cから1200 Cの育成後熱処理により向上することを判明した。陽電子消滅の結果は、亜鉛原子空孔の消失が、初期の結晶性向上に寄与していることを示している。
Cの育成後熱処理により向上することを判明した。陽電子消滅の結果は、亜鉛原子空孔の消失が、初期の結晶性向上に寄与していることを示している。
山本 悦嗣; 芳賀 芳範; 松田 達磨; 中村 彰夫; 摂待 力生*; 稲田 佳彦*; 菅原 仁*; 佐藤 英行*; 大貫 惇睦
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.187 - 190, 2002/11
チョクラルスキー法で単斜晶RbBi型構造の高純度単結晶UIrの育成に成功した。磁化測定からUIrはキュリー点 を持つイジング的な強磁性体であるとわかった。磁気モーメントは(010)面の[1 0
を持つイジング的な強磁性体であるとわかった。磁気モーメントは(010)面の[1 0 ![$=1]$](/search/images/LQ4TCXI.gif) 方向に配向していた。飽和モーメントは0.5
方向に配向していた。飽和モーメントは0.5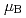 /Uであった。磁気的性質は磁化率,電気抵抗,ホール効果,熱電能にも反映し、大きく異方的であった。われわれはドハース・ファンアルフェン振動も測定した。検出したブランチはすべて9.6から32
/Uであった。磁気的性質は磁化率,電気抵抗,ホール効果,熱電能にも反映し、大きく異方的であった。われわれはドハース・ファンアルフェン振動も測定した。検出したブランチはすべて9.6から32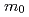 と重いサイクロトロン有効質量を持っていた。これらは電子比熱定数
と重いサイクロトロン有効質量を持っていた。これらは電子比熱定数  =49mJ/K
=49mJ/K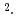 molと対応する。
molと対応する。
 Zn
Zn Cr
Cr Se
Se
飯久保 智*; 安井 幸夫*; 小田 啓介*; 大野 陽平*; 小林 義明*; 佐藤 正俊*; 加倉井 和久
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 71(11), p.2792 - 2799, 2002/11
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:56.87(Physics, Multidisciplinary)スピネル型化合物Cu Zn
Zn Cr
Cr Se
Se が示す異常ホール効果の特異な振舞とこの系が持つ特異な磁気構造の関連について中性子回折,NMR、及び他の磁気や輸送測定が行われた。その結果この系のコニカルテニウム磁気構造発達と異常ホール係数の関係が明らかになった。
が示す異常ホール効果の特異な振舞とこの系が持つ特異な磁気構造の関連について中性子回折,NMR、及び他の磁気や輸送測定が行われた。その結果この系のコニカルテニウム磁気構造発達と異常ホール係数の関係が明らかになった。
永田 正美*; 福本 直之*; 小川 宏明; 小川 俊英; 上原 和也; 新美 大伸*; 柴田 孝俊; 鈴木 喜雄; 三浦 幸俊; 粥川 尚之*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 41(11), p.1687 - 1694, 2001/11
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:38.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)コンパクトトロイド(CT)プラズマと外部磁場及びトカマクプラズマとの相互作用をJFT-2M並びにFACT装置を用いて実験的に研究した。JFT-2Mにおいて高速カメラによりCTプラズマの垂直方向のシフトを観測した。またダブルプローブ計測によりBe=1.0~1.4Tの範囲では、JFT-2Mプラズマのセパラトリックス近傍にまでCTプラズマが到達しており、さらにその後につづくトレーリングプラズマと言われる低速低密度プラズマの存在を明らかにした。さらにCTの磁場とトロイダル磁場とのリコネクションに関連した大振幅の揺動を観測した。FACT装置における外部磁場印加時のトリフト管中の挙動の観測結果をもとに、垂直方向のシフトはガン電流と外部磁場とのローレンツ力によるものであり、またトレーリングプラズマの侵入は分極電流による制動力がホール効果により減衰することによることを明らかにした。
伊藤 久義; T.Troffer*; C.Peppermuller*; G.Pensl*
Applied Physics Letters, 73(10), p.1427 - 1429, 1998/09
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:76.89(Physics, Applied)六方晶炭化珪素(4H-SiC)半導体におけるホウ素(B)アクセプターの電気的活性化に対する炭素(C)または珪素(Si)共注入効果を、ホール測定及びフォトルミネッセンス(PL)測定法を用いて調べた。この結果、B注入層の正孔濃度は、B単独注入の場合と比較し、C共注入を行うと増加し、Si共注入を行うと減少することが解った。C共注入を高温(800 C)で実施すると、室温C共注入と比べ、正孔濃度はより一層増加することを見出した。またPL測定より、浅い準位を有するBアクセプターに起因する波長383.9nmの発光線強度が、C共注入により増大することが解った。これらの結果は、B注入により作製したp型層の電気特性がC共注入により改善されることを示している。また本論文では、注入B原子の電気的活性化に対する共注入効果の機構についても議論する。
C)で実施すると、室温C共注入と比べ、正孔濃度はより一層増加することを見出した。またPL測定より、浅い準位を有するBアクセプターに起因する波長383.9nmの発光線強度が、C共注入により増大することが解った。これらの結果は、B注入により作製したp型層の電気特性がC共注入により改善されることを示している。また本論文では、注入B原子の電気的活性化に対する共注入効果の機構についても議論する。
田中 秋広*; 町田 昌彦
Physical Review Letters, 81(8), p.1746 - 1747, 1998/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:44.08(Physics, Multidisciplinary)最近、Wang,Z.は、多層層状量子ホール状態における相図の研究を行い、その結果をフィジカル・レビュー・レター誌に発表している。この論文は、この記事に対するコメントであり、彼の解析的計算に対し、より注意深い取り扱いが必要であると指摘し、さらにそれがもたらす物理的意味について言及するものである。Wangは、エッヂ状態のネットワークモデルから出発し、非線形シグマモデルを取り扱い、繰り込み群の手法を用いて、多くの興味深い重要な物理を指摘している。しかしながら、非線形シグマモデルへの写像における、トポロジカル項の存在は、より注意深い取り扱いが必要であり、主要な物理的結果に対し大きな影響を及ぼすものと考えられる。また、この研究により、様々な場面において出会う渦や欠陥等のトポロジカルな実体に対するより厳密な取り扱いが可能となる。
荒木 康史
no journal, ,
The main focus of this presentation is the theory of spin current generation in topological Dirac semimetals (TDSMs), the newly-found three-dimensional topological materials. TDSMs are characterized by pair(s) of doubly-degenerate nodal points (Dirac points) in their momentum-space band structures, which are observed by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) in Na Bi and Cd
Bi and Cd As
As . I focus on a lattice-strained TDSM, to obtain an additional contribution to the spin current generation. I propose that an electric field applied to the strained TDSM gives rise to a nonlinear spin Hall current, namely the spin current perpendicular to and quadratic in the electric field. The spin current response is obtained by the Boltzmann transport theory, regarding the strain as a pseudomagnetic field for the Dirac electrons. This nonlinear effect implies that one can obtain a rectified (dc) pure spin current out of an alternating (ac) electric field, which renders the TDSM an efficient spin-current injector.
. I focus on a lattice-strained TDSM, to obtain an additional contribution to the spin current generation. I propose that an electric field applied to the strained TDSM gives rise to a nonlinear spin Hall current, namely the spin current perpendicular to and quadratic in the electric field. The spin current response is obtained by the Boltzmann transport theory, regarding the strain as a pseudomagnetic field for the Dirac electrons. This nonlinear effect implies that one can obtain a rectified (dc) pure spin current out of an alternating (ac) electric field, which renders the TDSM an efficient spin-current injector.
荒木 康史
no journal, ,
Topological Dirac seimetals (TDSMs) form a new class of three-dimensional topological semimetals, characterized by pair(s) of doubly-degenerate nodal points (Dirac points) in their momentum(k)-space band structures. They show the intrinsic spin Hall effect (SHE), which comes from the k-space topology around the Dirac points. This spin Hall conductivity is topologically protected, while it cannot be easily tuned or enhanced at linear response. In order to overcome this problem, I theoretically propose that an electric field applied to a lattice-strained TDSM gives rise to an additional "nonlinear spin Hall current", namely the spin current perpendicular to and quadratic in the electric field. The spin current response is obtained by the Boltzmann transport theory, regarding the strain as a pseudomagnetic field for the Dirac electrons. The nonlinear SHE arises as the hybrid of the regular Hall effect driven by the pseudomagnetic field (strain) and the anomalous Hall effect from the k-space topology. This behavior implies that one can obtain a rectified (dc) pure spin current out of an alternating (ac) electric field, which renders the TDSM an efficient spin-current injector.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on spin pumping into a two-dimensional (2D) quantum spin Hall inslator (QSHI). Recent theories and experiments have demonstrated the QSHI phase in a monolayer of transition metal dichalcogenide 1T'-WTe2, which can be easily engineered in contrast to traditionally-known HgTe/CdTe and InAs/GaSb quantum wells. While the theory of spin pumping is well established in normal metals by focusing on the spin-dependent electron scattering at the interface, it is unreliable for topologically nontrivial interfaces in such systems. In the present work, we consider a junction of a ferromagnet and a 2D QSHI at its 1D edge, and demonstrate the pumping of angular momentum from the spin-precessing ferromagnet into the QSHI. Using the Floquet theory for the electrons on the helical edge states, we analytically show that the time-periodic precession of the magnetization drives a charge current on the edge, for the whole range of precession frequency. This edge current can be regarded as a consequence of the inverse spin Hall effect intrinsic to the QSHI, which converts the injected spin current into a transverse charge current. By varying the precession frequency of the magnetization and the coupling strength at the junction, we find a clear crossover between two regimes: the adiabatic regime, where the slow magnetization precession drives a quantized pumping, and the resonant regime, where the fast precession leads to a suppressed pumping. We also incorporate the effect of orbital dependence in the exchange coupling at the edge, and show numerically that it shifts the crossover point between the adiabatic and resonant regimes.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
The two-dimensional quantum spin Hall insulator (2D QSHI) is the most primitive but quite important realization of topological insulator. It shows the helical edge states protected by time-reversal symmetry, whereas the quantized spin Hall conductivity in the bulk. In the present work, we theoretically investigate the spin pumping from a precessing ferromagnet into a 2D QSHI thoroughly from the adiabatic to nonadiabatic regimes, both analytically and numerically. We analytically treat the dynamics of the edge-state electrons coupled to the precessing ferromagnet by the Floquet theory, and derive the pumped current as a function of the exchange energy and the precession frequency. We find that a heat bath for the edge electrons governs the transition between the adiabatic and nonadiabatic regime: when the edge electrons are coupled with a heat bath, their spin and energy can dissipate into the bath by a certain rate, eventually reaching a periodic steady state. The pumped current on the becomes quantized when the exchange energy exceeds the dissipation rate. We also calculate the edge current numerically on the 2D lattice model, and find that the bulk states in the QSHI effectively serves as the heat bath for the edge electrons.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on spin pumping into a two-dimensional (2D) quantum spin Hall inslator (QSHI). QSHI is a topological insulator in 2D exhibiting gapless helical edge stats, which are responsible for the quantized spin Hall conductivity. Recent theories and experiments have demonstrated the QSHI phase in a monolayer of transition metal dichalcogenide 1T'-WTe2, which can be easily engineered in contrast to traditionally-known HgTe/CdTe and InAs/GaSb quantum wells. While the theory of spin pumping is well established in normal metals by focusing on the spin-dependent electron scattering at the interface, it is unreliable for topologically nontrivial interfaces in such systems. In the present work, we consider a junction of a ferromagnet and a 2D QSHI at its 1D edge, and demonstrate the pumping of angular momentum from the spin-precessing ferromagnet into the QSHI. Using the Floquet theory for the electrons on the helical edge states, we analytically show that the time-periodic precession of the magnetization drives a charge current on the edge, for the whole range of precession frequency. This edge current can be regarded as a consequence of the inverse spin Hall effect intrinsic to the QSHI, which converts the injected spin current into a transverse charge current. By varying the precession frequency of the magnetization and the coupling strength at the junction, we find a clear crossover between two regimes: the adiabatic regime, where the slow magnetization precession drives a quantized pumping, and the resonant regime, where the fast precession leads to a suppressed pumping. We also incorporate the effect of orbital dependence in the exchange coupling at the edge, and show numerically that it shifts the crossover point between the adiabatic and resonant regimes.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on dynamical spin-to-charge conversion at the edge of a quantum spin Hall insulator (QSHI), namely a two-dimensional topological insulator with helical edge states. Interconversion between spin- and charge-related quantities has been a key idea in making use of magnetic materials, especially in the context of spintronics. QSHI is a typical system showing a universal charge-to-spin conversion behavior, namely the quantum spin Hall effect, whereas the spin-to-charge conversion therein is still not clearly understood. At a lateral heterojunction of a ferromagnet (FM) and a QSHI, it has been theoretically demonstrated that magnetization dynamics induces a charge current along the edge of QSHI; however, its mechanism from the viewpoint of spin-to-charge conversion still remains to be clarified. In order to understand the spin transfer and the spin-to-charge conversion mechanism in QSHI, we investigate the many-body dynamics of the electrons under the magnetization dynamics at the QSHI-FM junction. We analytically treat the electron dynamics in terms of the Floquet-Keldysh formalism, and compare two physical quantities present on the edge: the spin injection rate from the FM into the QSHI, and the charge current induced along the edge. Whereas the edge current seen in the previous works is reproduced, we find that it is not proportional to the spin injection rate, especially when the exchange interaction at the junction is strong enough. This relation implies that the spin-to-charge conversion in this system cannot be considered as the inverse spin Hall effect, while it can be rather seen as the inverse Edelstein effect, in which an electron spin accumulation at the junction is converted to a charge current. We also focus on the energy transfer at the junction, and interpret this phenomenon in terms of magnon exchange.
荒木 康史
no journal, ,
Spin current, namely the flow of spin angular momentum carried by electrons or spin waves in materials, plays the key role in designing next-generation spintronics devices. For efficient use of spin current, we need to lower the energy dissipation in the conversion process between charge and spin currents, and the transmission process of spin current. In this talk, I introduce my recent theoretical works for achieving low-dissipation spin-charge conversion and spin current transmission by making use of topological edge states. In particular, we have considered the roles of helical edge states on two-dimensional (2D) quantum spin Hall insulators (QSHIs) and 3D topological Dirac semimetals (TDSMs), which are (quasi-)1D channels protected by the bulk topology and hence robust against disorder. Helical edge states are suitable for spin-charge conversion and spin current transmission, due to their spin-helical nature, where the electrons propagate in directions depending on their spins (up/down). For spin-charge conversion, we consider spin pumping from a ferromagnet (FM) into a QSHI or a TDSM. The injected spin current is converted into a charge current flowing at the interface, and we evaluate the conversion rate from the spin current to the charge current. As a result, we find that the conversion rate is enhanced under a strong exchange coupling at the interface, around 100 times larger than the conversion rate at 2D interfaces of complex oxides. For spin current transmission, we consider the transmission between two FMs (FM1/FM2) mediated by the helical edge states of a QSHI or a TDSM. We evaluate the spin current injected from FM1 into FM2 analytically and numerically, which exerts a torque on FM2 switching its magnetization. As a result, we find that the spin current is semi-quantized depending on the number of edge channels, and is robustly transmitted against disorder over a long range.